Networking is an essential aspect of today’s digital world. It’s essential to understand the default gateway concept to establish and manage a network. This blog post will guide you through the basics of default gateway and its practical applications.
What is a Default Gateway?
A default gateway is the entry point to a network. It is the device that connects the local network to the larger, public network. It allows communication between devices on the same network and devices on different networks. The default gateway is typically a router, which acts as a traffic cop, directing incoming and outgoing network traffic.
How Does it Work?
The default gateway works by forwarding IP packets between the local network and the public network. When a device on the local network wants to communicate with a device on a different network, it sends the IP packet to the default gateway, which then forwards it to the appropriate device on the public network.
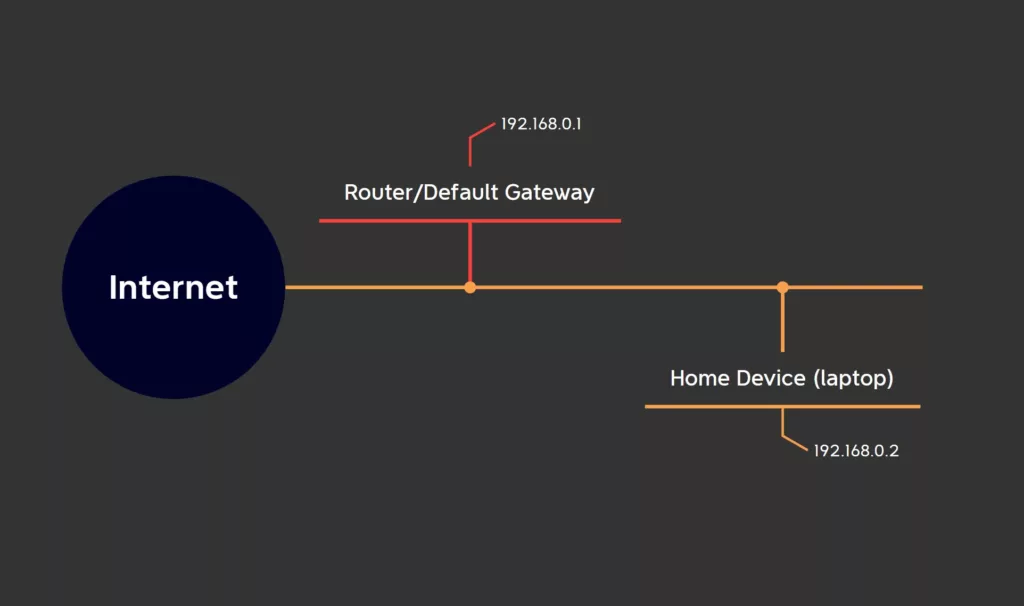
Practical Use-Cases
Home Networking
Home networks typically use a router as the default gateway. The router provides Internet connectivity for all devices in the home network, such as laptops, smartphones, and smart home devices. The router acts as the IP address of the gateway in the home network, allowing all devices to communicate with each other and with the Internet.
Enterprise Networking
Enterprise networks are typically much larger than home networks and can span multiple locations. They use routers, switches, and firewalls to manage network traffic and provide secure connectivity to the Internet. The default gateway in an enterprise network is typically a router or firewall that provides secure connectivity to the Internet and allows communication between devices on the same network and devices on different networks.
Tools
There are several hardware and software tools that can be used to manage and monitor the default gateway in a network. These tools include:
- Router Configuration Utilities: These tools, such as the web-based interface for a home router, allow users to configure the default gateway, manage network settings, and monitor network traffic.
- Network Monitoring Software: These tools, such as Wireshark and Nagios, allow users to monitor network traffic, troubleshoot connectivity issues, and view information about the default gateway and other network devices.
- Command Line Tools: These tools, such as the ping and traceroute commands, allow users to test connectivity to the default gateway and other network devices and view information about network routes.
Tips for Power and Advanced Users
- Secure Your Default Gateway: To protect your network from external threats, make sure to change the default login credentials for your router and enable WPA2 encryption for Wi-Fi networks.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Use network monitoring software to monitor network traffic and detect potential security threats or performance issues.
- Keep Your Router’s Firmware Up-to-Date: Regularly check for firmware updates for your router and install them to ensure that you have the latest security patches and performance enhancements.
- Test Connectivity Regularly: Use the ping and traceroute commands to regularly test connectivity to the default gateway and other network devices to ensure that they are functioning correctly.
- Use VLANs to Segment Your Network: If you have a large network, use VLANs to segment the network into smaller, more manageable subnets. This can improve network security and performance.
Summary
The default gateway is an essential component of networking. It allows communication between devices on the same network and devices on different networks. Understanding and properly configuring the default gateway can improve network security, performance, and connectivity. Power and advanced users can use tools such as router configuration utilities, network monitoring software, and command line tools to manage and monitor the default gateway. By following the tips provided in this blog post, users can secure their networks and improve their overall networking experience.
Next, it’s recommended to learn about network address translation (NAT), which allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address. It’s also a good idea to familiarize yourself with the different types of routers, switches, and firewalls and their functions in a network.
Challenge
Take a look at your home network and how your router is configured. Then use ping and traceroute to follow the traffic flow. You can also use Wireshark or tcpdump for more in-depth information and packet analysis.



